Theory and Defination :
Acetoacetic-Ester Condensation is a chemical reaction where ethyl acetoacetate is alkylated at the α-carbon to both carbonyl groups and then converted into a ketone, or more specifically an α-substituted acetone. This is very similar to malonic ester synthesis.
Acetoacetic ester synthesis is a synthetic procedure used to convert a compound that has the general structural formula 1 into a ketone that has the general structural formula 2.

Acetoacetic ester synthesis is a synthetic procedure used to convert a compound that has the general structural formula 1 into a ketone that has the general structural formula 2.

where as,
R1 is alkyl group
L is Leaving group
The group -CH2COCH3 in 2 is contributed by an acetoacetic ester, hence the term acetoacetic ester synthesis.
 where R2 is alkyl , aryl group
where R2 is alkyl , aryl group
Acetoacetic ester synthesis consists of four consecutive reactions that can be carried out in the same pot.
reaction 1: acid-base reaction
reaction 2: nucleophilic substitution
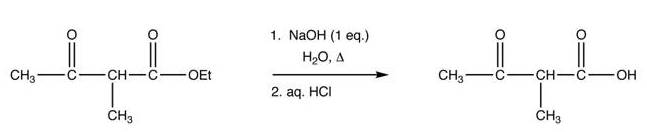
reaction 3: ester hydrolysis (using saponification)
reaction 4: decarboxylation
Taking an example as below ;
reaction 1: acid-base reaction
reaction 2: nucleophilic substitution
reaction 3: ester hydrolysis (using saponification)
reaction 4: decarboxylation
Taking an example as below ;
As above mentioned follow the steps
reaction 1: acid-base reaction
reaction 2: nucleophilic substitution
reaction 3: ester hydrolysis (using saponification)
reaction 4: decarboxylation
A more direct method to convert 3 to 4 is the reaction of 3 with the enolate ion (5) of acetone.

However, the generation of 5 from acetone quantitatively in high yield is not an easy task because the reaction requires a very strong base, such as LDA, and must be carried out at very low temperature under strictly anhydrous conditions.
Mechanism :
A strong base deprotonates the dicarbonyl α-carbon. This carbon is preferred over the methyl carbon because the formed enolate is conjugated and thus resonancestabilized. The carbon then undergoes nucleophilic substitution. When heated with aqueous acid, the newly alkylated ester is hydrolyzed to a β-keto acid, which isdecarboxylated to form a methyl ketone .