Theory and Defination :
E .J.Corey and D.Seebach introduced a concept of " umplong " which is a German term and had a meaning of inversion of reactivity .In other words we can say that it is a chemical modification of a functional group with the aim of the reversal of polarity of that group . Seebach-Corey gives a simplest method to synthesize 1,2-, 1,4-, 1,6- hetero atom substitution patterns. Their concept is based on the organic molecules contains hetero-atoms which polarize carbon skeletons by virtue of their electro negativity. Therefore, in organic reactions, the majority of new bonds are formed between atoms of opposite polarity. This can be considered to be the "normal" mode of reactivity.Hence they develop methods to induce umpolung in organic reactions.General Reaction :

Mechanism :
The Corey-Seebach Reaction allows a reversal of the normal reactivity of acyl carbon atoms, which combine only with nucleophiles. The German term "Umpolung" is widely used for this inversion of reactivity.
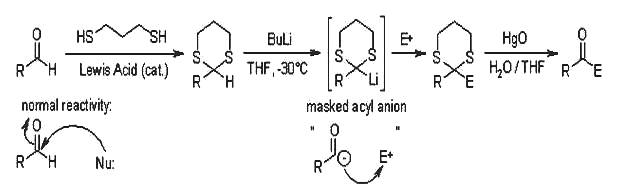
The lithiated 1,3-dithiane can be viewed as an masked acyl anion that is able to react with various electrophiles.

The acidity difference of hydrogen atoms adjacent to divalent sulfur compared to oxygen stems from the greater stabilizability of sulfur and the longer C-S-bond length; d-orbitals are not involved. In most cases treatment of dithianes with n-BuLi at temperatures of -30 °C is sufficient for the preparation of the lithio-derivatives. With pKA values of approximately 30, lithiated dithianes can react with aldehyde or ketones, epoxides and acid derivatives, but also with alkyl halides without competing elimination reactions.

Umpolung offers access to a wide range of products, especially 1,2-diketones and α-hydroxy ketones, products that cannot be obtained using the normal reactivity (for example through aldol addition).

1,3-Dithianes are readily prepared from aldehydes (for an overview, see 1,3-dithianes as protecting group) and offer high stability towards acids and bases. Therefore, use of the S,S-acetal unit is especially useful in multistep synthesis. A crucial step is the hydrolysis of S,S-acetals, the difficulty of which is due to the excellent nucleophilicity of sulfur.

Only irreversible removal of the dithiol or of the solvolysis products can push the equilibrium to the right. Methods of choice are transacetalization to a highly reactive carbonyl derivative, alkylation to sulfide, oxidation of the thiol (for recent methods see deprotection of 1,3-dithianes) and formation of metal thiolates, for which mercury(II) salts are frequently used.
Example and Applications :

2) Anion Relay Chemistry: An Effective Tactic for Diversity Oriented Synthesis